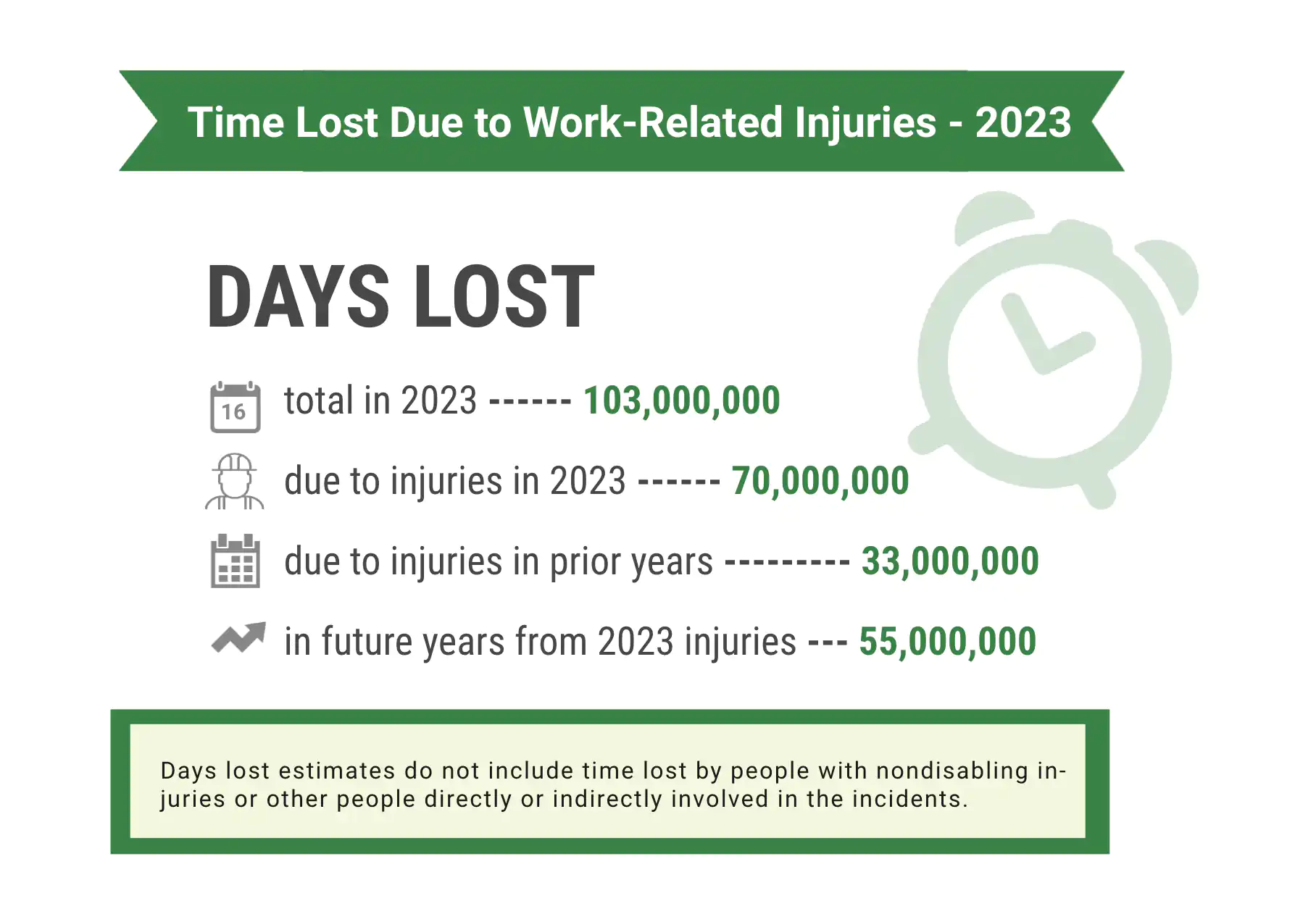
Long-term costs from injuries at work
Long-term costs capture the ongoing financial impact of workplace injuries, potentially hindering your business growth into the future. Some of these long-tail costs include:
- Higher business insurance premiums. If your business has a history of injured workers, it could increase your insurance costs moving forward.
- Damage to your business reputation. A dangerous workplace could make it hard to hire more talent when you need them. And if word gets out, it could also result in the potential loss of customer trust and sales.
- Low morale. If your employees don’t feel safe and protected at work it could lead to more staff turnover (and HR costs) and lower productivity.
These costs can be particularly devastating for small businesses operating on tight margins. Implementing proactive safety measures and fostering a workplace safety culture is essential to mitigate these expenses.
If you want to see what workplace injury costs would look like for your business, OSHA’s Individual Injury Estimator can help you see some specific numbers.
Most common workplace injuries in small businesses
According to data from the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, the most frequent workplace injuries that result in time away from work include:
- Sprains, strains and tears (24%): Often due to falls, trips, slips, overexertion in lifting, pushing or other repetitive movements.
- Soreness and pain (15%): Sprains, strains and tears, soreness and pain are commonly attributed to overexertion, falls, slips, trips and contact with objects and equipment.
- Cuts, lacerations and punctures (8%): Frequently associated with tools, equipment and sharp objects, both handheld and stationary.
- Bruises and contusions (7%): Typically resulting from slips, trips and being struck by objects.
- Fractures (7%): Often caused by falls, slips or equipment-related.
Proactively addressing these injury types through prevention strategies can significantly reduce workplace injuries and associated costs.
Hidden injury risks for small businesses
Not every workplace risk is immediately evident. These subtle dangers are just a few that can often be overlooked:
Mental health and workplace stress
Workplace stress can significantly impact employee well-being and productivity.
According to an American Psychological Association survey, 54% of U.S. workers cited job insecurity as a major stress factor. And 39% expressed concern about potential job loss within the next year due to changes in government policies. Financial stress compounds these issues, costing U.S. employers around $183 billion annually.
Ergonomic issues and remote work
Many small businesses overlook ergonomic setups for remote workers, which can lead to repetitive strain injuries and back pain. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) notes that ergonomic disorders are among the most frequently reported workplace injuries.
Inadequate safety training
Small businesses sometimes skip or minimize safety training due to limited resources or time constraints. However, insufficient training can increase injury risks and may result in regulatory penalties or legal costs if an incident occurs.
How to prevent workplace injuries
Small businesses can significantly reduce the costs of occupational injuries with practical, proactive prevention strategies. Some best practices that could help improve safety for your workers include:
Regular safety audits
Routine inspections can significantly reduce workplace injuries by identifying potential hazards before they become serious issues.
- Schedule regular inspections. Check for hazards like slippery surfaces, clutter or malfunctioning equipment.
- Maintain detailed records. Document findings from safety audits and swiftly address any hazards.
- Involve employees. Include your team in the audit process to foster a culture of safety awareness.
Employee safety training
Implementing a health and safety program could result in as much as a 20% (or more) reduction in injury and sickness rates, with a return of $4-$6 for every $1 invested. To better train your team:
- Conduct comprehensive sessions. Regularly host training tailored specifically to your industry.
- Update training materials frequently. Reflect the latest safety standards and best practices.
- Engage your team. Use interactive sessions, role-playing scenarios and real-world examples to keep employees interested.
- Communicate importance. Reinforce the value of safety training to ensure high participation.
Ergonomic workspaces
Create an ergonomic workplace to help reduce injuries, boost productivity and increase employee satisfaction.
- Provide adjustable equipment. Ensure desks and chairs can be tailored to individual needs.
- Regularly evaluate workstations. Check and adjust employee setups to maintain optimal ergonomic conditions. OSHA offers an evaluation checklist to help you.
- Encourage regular breaks. Promote stretching and short breaks to help reduce repetitive strain injuries.
Clear communication and reporting
Open and effective communication can help identify risks early and prevent accidents.
- Establish clear reporting procedures. Make it easy to report hazards or incidents.
- Ensure anonymity if needed. Encourage honest and proactive reporting by safeguarding confidentiality.
- Regularly reinforce the importance. Continuously communicate that hazard reporting is vital for workplace safety.
- Act promptly on reports. Address reported hazards transparently and swiftly to build trust with your workers.
How business insurance can help you manage risk and costs
Business insurance is essential to help your business manage workplace injury risks and costs. Here’s how different types of insurance that can help protect your small business:
Workers’ Compensation insurance
Workers’ compensation insurance is usually required if you have employees. But even if it’s not, it can help protect your business from the costs of medical treatment, rehab costs and lost wages when employees suffer a work-related illness or injury.
For employers, workers’ comp also offers some legal protection. This type of coverage typically includes some protection from work-related injury employee lawsuits to help reduce legal liabilities and associated costs.
General Liability insurance
General liability coverage can help cover claims if a non-employee, like a customer or someone walking past your business, suffers a physical injury, property damage or advertising injury caused by you or your workers.
For instance, if a customer slips and falls on your premises, a general liability insurance policy could help cover medical costs and legal expenses so you aren’t footing the bill alone.**
Commercial Auto Insurance
Commercial auto insurance can help protect businesses from liabilities after accidents or damage caused by company-owned vehicles.
Motor vehicle accidents during work-related activities — such as deliveries, driving to business meetings, or running job-related errands — can be considered workplace injuries.